Gel electrophoresis and DNA sequencing 3/29
Date/Title: 3/29/18 Gel electrophoresis and DNA sequencing
Purpose: The purpose of this lab was to run the gel electrophoresis to find out if there was any DNA. Once we found the DNA, we could amplify the DNA and observe any overlapping areas that can help us identify the DNA.
Materials:
- Gel with cell wells
- electrophoresis apparatus
- Loading Buffer
Procedure:
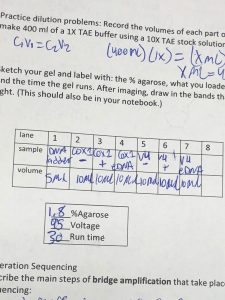
- Make 400 ml of a 1X TAE buffer using 10X TAE stock solution (40 ml).
- Add gel to gel electrophoresis chamber and pour in the buffer.
- Add 5 μL of Ladder to a cell well (for comparison)
- Add 10 μL of each PCR product to their designated wells.
- Put the lid on the chamber with the wires connected.
- Set the power supply to 95 volts. Run for 30 minutes.
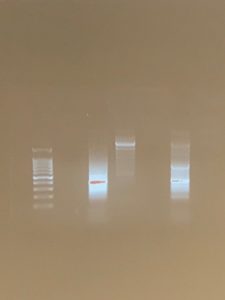
- Remove the gel and scan with UV imaging to search for DNA.
Next Generation Sequencing:
- add adaptors to ends of DNA fragments
- attach fragments to flowcells
- The strand should bend in the PCR extension and attach to a second oligo, forming a bridge.
- A polymerase synthesizes the reverse strand
- Each strand forms a new bridge and this results in DNA strand clones.
Data:
results/conclusion:
The chelex procedure was the most successful. This was surprising because the powersoil method was supposed to yield the best results. A reason why the powersoil method may have been less successful could be the use of dry soil (instead of the non-flooded plate like the chelex procedure). We completed the powersoil procedure and received positive results from the positive V4 primer and eDNA. There was a source of error because the location of our DNA was too far back. The V4 primers should be further up and the COX1 should be further back. Also our DNA was not very distinct and it was very fuzzy. This also indicates a possible error that may or may not be due to our protocol. We sequenced the amplified DNA and the next step would be to analyze the DNA and find overlapping areas. This is important because these overlapping areas can be used to classify the DNA and match it with a ciliate.
Storage: lab room, labeled CLK.