The long-range goal of our research is to develop and advance nanoscale imaging techniques for extremely-high resolution sensing (chemical, thermal, optical, and magnetic) in practical complex environments and see the eventual adoption of these techniques by the scientific community in both academic and industrial settings.
The specific research is in two areas. One is to develop a transformative nanoscale chemical and thermal imaging microscopy based on advanced plasmonic fiber probes and use it to study materials in application-relevant environments (ambient and liquid). The other is to study surface reaction mechanisms on various catalytic and optic materials at the molecular level and the microscale level.
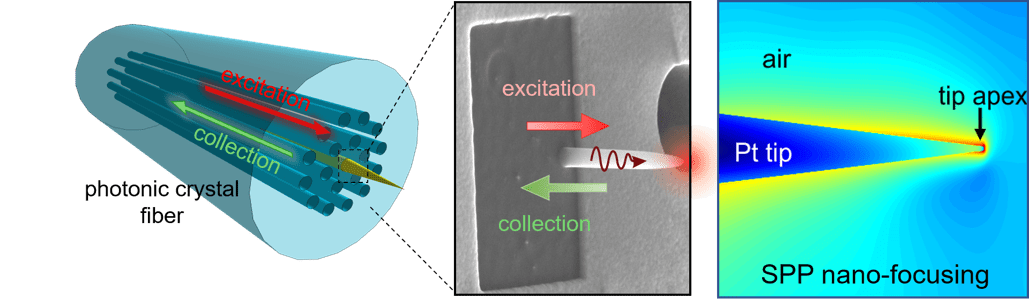
Nanofocusing of Light for Chemical Imaging
The goal of the research is to develop a transformative nanoscale chemical imaging microscopy based on advanced plasmonic fiber probes and use it to study optical materials and the photo-chemistry of catalysts in application-relevant environments (ambient and liquid). A simple and straightforward method of efficient coupling and focusing of the light from optical fiber photonic mode to the nanoscale plasmonic mode was developed for nanoscale chemical imaging. The device involved is a needle-like metal nano-antenna fabricated on the end facet of a photonic crystal fiber.
Publications
K. Minn, A. Anopchenko, C. Chang, R.i Mishra, J. Kim, Z. Zhang, Y. Lu, S. Gwo, and H. H. Lee, Enhanced Spontaneous Emission of Monolayer MoS2 on Epitaxially Grown Titanium Nitride Epsilon-Near-Zero Thin Films, 2021, DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00491
K. Minn, B. Birmingham, B. Ko, H.H. Lee, Z. Zhang, Interfacing photonic crystal fiber with metallic nanoantenna for enhanced light nano-focusing, Photonics Research,9(2), 2021,252-258; https://doi.org/10.1364/PRJ.411583, highlighted by Spotlight on Optics.
K. Minn, H. H. Lee, and Z. Zhang, Enhanced subwavelength coupling and nano-focusing with optical fiber-plasmonic hybrid probe, Optics Express, 27 (2019), 38098-38108 (2019), DOI 10.1364/OE.27.038098
Tip-enhanced Raman scattering on 2D materials
The objective is to advance molecular-level chemical identification of molecules on non-traditional Raman scattering materials, MoS2, for heterogeneous catalysis using a combination of the most advanced Raman spectroscopies. This research plan addresses fundamental questions that are essential for advancing SERS on newly emerged Raman-active transition metal dichalcogenides. The proposed work will advance the field of catalysis research with high sensitivity (submonolayer) and high spatial (~10 nm) resolution.
Publications
B. Birmingham, Z. Liege, N. Larson, W. Lu, K.T. Park, Lee, H.H. Lee, D.V. Voronine, M.O. Scully and Z. Zhang, Probing Interaction between Individual Submonolayer Nanoislands and Bulk MoS2 Using Ambient TERS, J. Phys.Chem. C 2018 122(5) 2753-2760
B.A. Ko, A. Sokolov, M.O. Scully, Z. Zhang, and H.H. Lee, Enhanced Four-Wave Mixing Process Near the Excitonic Resonances of Bulk MoS2, Photonics Research, 7 (2019) 251-259, DOI 10.1364/PRJ.7.000251
D.V. Voronine, Z. Zhang, A.V. Sokolov, and M.O. Scully, Surface-Enhanced FAST CARS: En Route to Quantum Nano-Biophotonics, Nanophotonics, 2017, Invited, https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2017-0066 .
Z. He, D.V. Voronine, A.M. Sinyukov, Z.N. Liege, B. Birmingham, A.V. Sokolov, Z. Zhang, and M.O. Scully, Tip-enhanced Raman scattering on bulk MoS2 substrate, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 23 (2017), 4601006, DOI 10.1109/JSTQE.2016.2611591
A.M. Alajlan, D.V. Voronine, A.M. Sinyukov, Z. Zhang, A.V. Sokolov, and M. O. Scully, Gap-mode enhancement on MoS2 probed by functionalized tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, Appl. Phys. Lett., 109 (2016) 133106
Aluminum plasmonic nanoparticles for sensor
We developed a simple and efficient method of synthesizing two-dimensional (2D) aluminum (Al) nanocrystals from commercially available Al foil using ultrasonic exfoliation under ambient environment. Al nanostructures can be used for optical sensing and imaging applications.
Publications
W. Lu, B. Birmingham, D. Voronine, D. Stolpman, S. Ambardar, D. Altunoz Erdogan, E. Ozensoy, Z. Zhang, T. Solouki, From aluminum foil to two-dimensional nanocrystals using ultrasonic exfoliation, J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 14, 7746–7755.
J. Kunz, D.V. Voronine, W. Lu, Z. Liege, H.H. Lee, Z. Zhang, and M.O. Scully, Aluminum plasmonic nanoshielding in ultraviolet inactivation of bacteria, Scientific Reports, 2017, 7 (2017) 9026
Photo-reaction on monolayer MoS2
Monolayer MoS2 has become a very promising two-dimensional materials for photo-related applications, potentially serving as the basis for an ultrathin photodetector, switching device, or transistors due to its strong interaction with light in ambient conditions. Establishing the impact of individual ambient gas components on the optical properties of MoS2 is a necessary step toward application development.
Publications
B. Birmingham, J. Yuan, M. Filez, D. Fu, J. Hu, J. Lou, M.O. Scully, B.M. Weckhuysen, Z. Zhang, Probing the Effect of Chemical Dopant Phase on Photoluminescence of Monolayer MoS2 Using in Situ Raman Micro-Spectroscopy. J.Phys. Chem. C 2019 123, 25, 15738-15743
B. Birmingham, J. Yuan, M. Filez, D. Fu, J. Hu, J. Lou, M.O. Scully, B.M. Weckhuysen, Z. Zhang, Spatially-Resolved Photoluminescence of Monolayer MoS2 under Controlled Environment for Ambient Optoelectronic Applications, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2018, 1 (11), pp 6226–6235
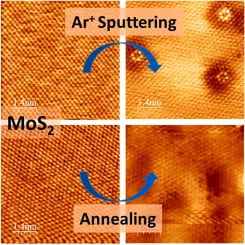
Defect engineering on MoS2
MoS2 is the most promising electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The objective is to understand the defects creation on MoS2 at an atomic-level and their role in HER and optoelectronic applications.
Publications
W. Lu, B. Birmingham, Z. Zhang, Defect Engineering on MoS2 Surface with Argon Ion Bombardments and Thermal Annealing, Applied Surface Science, 532, (2020) 147461; doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.
Catalytic Reactions on TiO2
The research objective of this project is to understand the individual reaction steps of adsorbates on TiO2 thin films in the visible-light photodegradation of organic air pollutants. This research plan addresses fundamental questions that are essential for the rational design of catalysts that efficiently carry out the photo-oxidation of organic pollutants.
Publications
K. Zhu, Y. Xia, Z. Zhang, K. T. Park, Photo-stimulated desorption of trimethyl acetic acid on cross-linked (1 × 2) TiO2(110) probed by scanning tunneling microscopy, Applied Surface Science,511,(2020) 1455553; DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.14555
M. Tang, Z. Zhang and Q. Ge, A DFT-based study of surface chemistries of rutile TiO2 and SnO2 (110) toward formaldehyde and formic acid, Catalysis Today, 274 (2016) 103-108
X. Yu, Z. Zhang, C. Yang, F. Bebensee, S. Heissler, A. Nefedov, M. Tang, Q. Ge, L. Chen, B. Kay, Z. Dohnalek, Y.Wang, Interaction of Formaldehyde with the Rutile TiO2(110) Surface: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study, J. Phys. Chem. C, 120 (2016) 12626–12636
Click here for a full list of publications.
We thank the following orgnizations for financial support of these works: